Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, the East China Sea, China, North Korea,South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south. The kanji that make up Japan's name mean "sun origin", and it is often called the "Land of the Rising Sun".
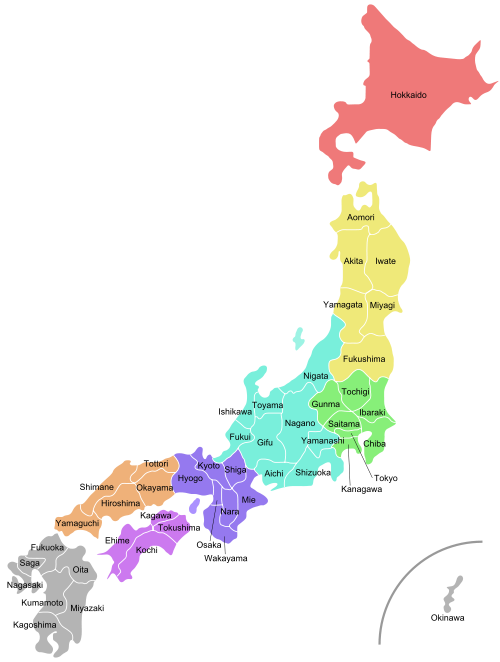
Japan is a stratovolcanic archipelago of 6,852 islands. The four largest are Honshu, Hokkaido, Kyushu and Shikoku, which make up about ninety-seven percent of Japan's land area. The country is divided into 47 prefectures in eight regions. The population of 126 million is theworld's tenth largest. Japanese make up 98.5% of Japan's total population. Approximately 9.1 million people live in the core city of Tokyo,the capital city of Japan, which is the sixth largest city proper in the OECD and the fourth leading global city in the world.[11] The Greater Tokyo Area, which includes Tokyo and several surrounding prefectures, is the world's largest metropolitan area with over 35 million residents and theworld's largest urban agglomeration economy.
Archaeological research indicates that Japan was inhabited as early as the Upper Paleolithic period. The first written mention of Japan is inChinese history texts from the 1st century AD. Influence from other regions, mainly Imperial China and later from Western Europe, has characterized Japan's history. From the 12th century until 1868, Japan was ruled by successive feudal military shoguns who ruled in the name of the Emperor. Japan entered into a long period of isolation in the early 17th century, which was ended in 1853 when a United States fleetpressured Japan to open to the West. Nearly two decades of internal conflict and insurrection followed before the Meiji Emperor was restored as head of state in 1868 and the Empire of Japan was proclaimed, with the Emperor as a divine symbol of the nation. In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, victories in the First Sino-Japanese War, the Russo-Japanese War and World War I allowed Japan to expand its empire during a period of increasing militarism. The Second Sino-Japanese War of 1937 expanded into part of World War II in 1941, which came to an end in 1945 following the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki. Since adopting its revised constitution in 1947, Japan has maintained a unitaryconstitutional monarchy with an Emperor and an elected legislature called the National Diet.
Japan is a member of the UN, the G7, the G8, and the G20 and is considered a great power. The country has the world's third-largest economy by nominal GDP and the world's fourth-largest economy by purchasing power parity. It is also the world's fourth-largest exporter andfourth-largest importer. Although Japan has officially renounced its right to declare war, it maintains a modern military with the world's eighth largest military budget, used for self-defense and peacekeeping roles. Japan is a developed country with a high standard of living andHuman Development Index whose population enjoys the highest life expectancy, the third lowest infant mortality in the world, and ranked first in the number of Nobel Laureates of any country in Asia. Japan is ranked first in the Country Brand Index,ranked sixth in the Global Competitiveness Report 2015–2016 and is the highest-ranked Asian country in the Global Peace Index. Japan was the first country in Asia to host the Summer and Winter Olympic Games.
Japan has a total of 6,852 islands extending along the Pacific coast of East Asia. The country, including all of the islands it controls, lies between latitudes 24° and 46°N, and longitudes 122° and 146°E. The main islands, from north to south, are Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku and Kyushu. TheRyukyu Islands, which includes Okinawa, are a chain to the south of Kyushu. Together they are often known as the Japanese archipelago.
About 73 percent of Japan is forested, mountainous, and unsuitable for agricultural, industrial, or residential use. As a result, the habitable zones, mainly located in coastal areas, have extremely high population densities. Japan is one of the most densely populated countries in the world.
The islands of Japan are located in a volcanic zone on the Pacific Ring of Fire. They are primarily the result of large oceanic movements occurring over hundreds of millions of years from the mid-Silurian to the Pleistocene as a result of the subduction of the Philippine Sea Plate beneath the continental Amurian Plate and Okinawa Plate to the south, and subduction of the Pacific Plate under the Okhotsk Plate to the north. Japan was originally attached to the eastern coast of the Eurasian continent. The subducting plates pulled Japan eastward, opening the Sea of Japan around 15 million years ago.
Japan has 108 active volcanoes. During the twentieth century several new volcanoes emerged, including Shōwa-shinzan on Hokkaido and Myōjin-shōoff the Bayonnaise Rocks in the Pacific. Destructive earthquakes, often resulting in tsunami, occur several times each century. The 1923 Tokyo earthquake killed over 140,000 people. More recent major quakes are the 1995 Great Hanshin earthquake and the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake, a 9.0-magnitude quake which hit Japan on March 11, 2011, and triggered a large tsunami. Due to its location in the Pacific Ring of Fire, Japan is substantially prone to earthquakes and tsunami, having the highest natural disaster risk in the developed world.
Japan has nine forest ecoregions which reflect the climate and geography of the islands. They range from subtropical moist broadleaf forests in the Ryūkyū and Bonin Islands, to temperate broadleaf and mixed forests in the mild climate regions of the main islands, to temperate coniferous forests in the cold, winter portions of the northern islands. Japan has over 90,000 species of wildlife, including the brown bear, the Japanese macaque, the Japanese raccoon dog, the Large Japanese Field Mouse, and the Japanese giant salamander. A large network of national parkshas been established to protect important areas of flora and fauna as well as thirty-seven Ramsar wetland sites. Four sites have been inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage List for their outstanding natural value.
| Rank | Name | Prefecture | Pop. | Rank | Name | Prefecture | Pop. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Tōkyō  Yokohama | 1 | Tōkyō | Tōkyō | 8,949,447 | 11 | Hiroshima | Hiroshima | 1,174,209 |  Ōsaka  Nagoya |
| 2 | Yokohama | Kanagawa | 3,689,603 | 12 | Sendai | Miyagi | 1,045,903 | ||
| 3 | Ōsaka | Ōsaka | 2,666,371 | 13 | Kitakyūshū | Fukuoka | 977,288 | ||
| 4 | Nagoya | Aichi | 2,263,907 | 14 | Chiba | Chiba | 962,130 | ||
| 5 | Sapporo | Hokkaidō | 1,914,434 | 15 | Sakai | Ōsaka | 842,134 | ||
| 6 | Kōbe | Hyōgo | 1,544,873 | 16 | Niigata | Niigata | 812,192 | ||
| 7 | Kyōto | Kyōto | 1,474,473 | 17 | Hamamatsu | Shizuoka | 800,912 | ||
| 8 | Fukuoka | Fukuoka | 1,463,826 | 18 | Kumamoto | Kumamoto | 734,294 | ||
| 9 | Kawasaki | Kanagawa | 1,425,678 | 19 | Sagamihara | Kanagawa | 717,561 | ||
| 10 | Saitama | Saitama | 1,222,910 | 20 | Shizuoka | Shizuoka | 716,328 | ||
EmoticonEmoticon